Luft-Fahrzeug-Gesellschaft
LFG V 3
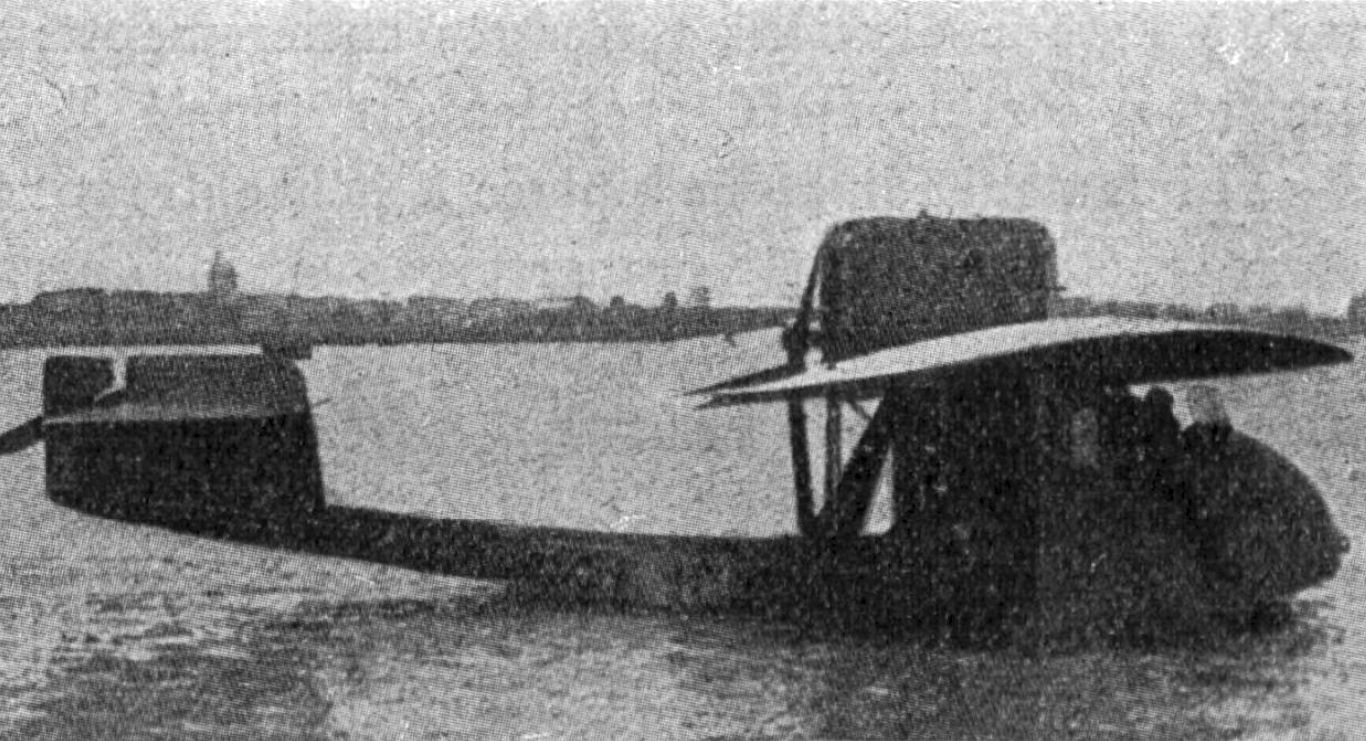
The LFG V 3 was a single‑engine, two‑seat biplane produced by the German firm Luft‑Fahrzeug‑Gesellschaft (LFG) during the final years of World War I. Designed in 1917 as a trainer and reconnaissance platform, the V 3 incorporated LFG’s characteristic “double‑wing” (Doppeldecker) layout with slightly staggered upper and lower wings and a wooden frame covered in fabric. Power came from a 120 hp Mercedes D.II inline engine driving a two‑bladed wooden propeller, giving the aircraft a top speed of about 140 km/h and a service ceiling of 4,500 m. Its open cockpit provided excellent visibility for both pilot and observer, while the simple control system and forgiving handling made it popular with flight schools.
Although only a small batch—approximately 30 airframes—were built before the armistice halted production, the V 3 demonstrated LFG’s ability to adapt its larger bomber designs to lighter roles. The aircraft’s straightforward construction influenced post‑war civil trainers in Germany and contributed to the development of the more advanced LFG V 13 series. Today the V 3 is remembered as a modest yet pivotal step in the transition from wartime combat aircraft to peacetime aeronautical training.
Although only a small batch—approximately 30 airframes—were built before the armistice halted production, the V 3 demonstrated LFG’s ability to adapt its larger bomber designs to lighter roles. The aircraft’s straightforward construction influenced post‑war civil trainers in Germany and contributed to the development of the more advanced LFG V 13 series. Today the V 3 is remembered as a modest yet pivotal step in the transition from wartime combat aircraft to peacetime aeronautical training.
Classification
Production & History
- First Flight
- 1919
Design & Classification
- Primary Use
- Country of Origin
- Manufacturer
- Luft-Fahrzeug-Gesellschaft
- Wikidata ID
- Q117324221