Piasecki Aircraft Corporation
Piasecki VZ-8 Airgeep
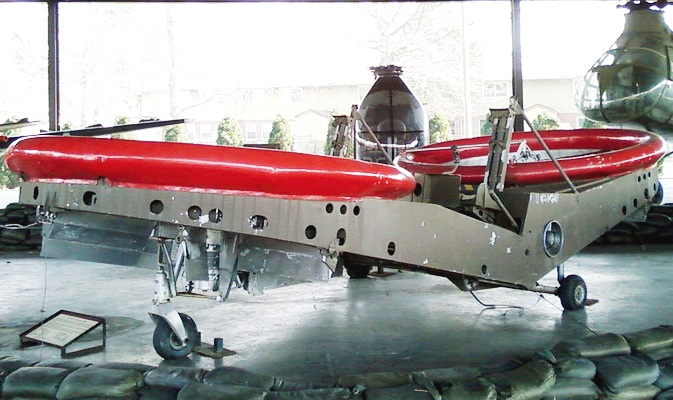
The Piasecki VZ‑8 Airgeep was a groundbreaking experimental VTOL aircraft developed in the late 1950s by Piasecki Aircraft Corporation for the United States Army. Conceived under the Army’s quest for a lightweight, all‑terrain transport capable of operating from swamp, jungle, and snow, the Airgeep first flew on 13 June 1958. Its design combined a compact twin‑boom airframe with two large, coaxial rotors mounted on either side of a central fuselage, providing lift without the need for conventional wings or tail surfaces. Power came from a single Lycoming O‑360 engine driving both rotors through a gearbox, allowing the craft to hover, transition to forward flight, and land on very short or unprepared surfaces. Although only three prototypes were built, the VZ‑8 demonstrated the feasibility of low‑cost, rotor‑driven ground‑effect vehicles and influenced later concepts such as the Hiller V‑1000 and modern tilt‑rotor platforms. Its significance lies in illustrating how rotorcraft technology could be adapted for amphibious and highly mobile battlefield logistics, marking an important step in the evolution of vertical‑takeoff aircraft and inspiring future research into hybrid air‑ground vehicles. The Airgeep remains a cult legend among aviation enthusiasts.
Classification
Production & History
- Units Produced
- 2
- First Flight
- 1962
Design & Classification
- Manufacturer
- Piasecki Aircraft Corporation
- Wikidata ID
- Q3656053