Short Brothers
Short Type 184
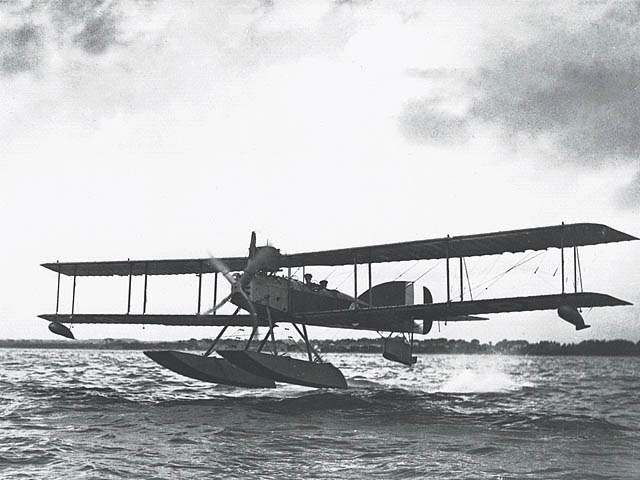
The Short Type 184 was a two‑seat, single‑engine biplane torpedo bomber and reconnaissance aircraft built by the British firm Short Brothers during the First World War. First flown in 1915, the type entered service with the Royal Naval Air Service in early 1916 and quickly became the navy’s principal floatplane. Powered by a 260‑hp Sunbeam or later a 300‑hp Hispano‑Suiza engine, the aircraft featured equal‑span wings, a wooden frame covered with fabric, and twin floats that allowed operation from water as well as from aircraft carriers equipped with a temporary deck. Its 64‑inch (1.63 m) torpedo load made it the first land‑based plane to successfully drop a torpedo against a moving ship, a feat achieved on 12 August 1915 when Flight Lieutenant C. R. Samson sank the Turkish cruiser Marmara. Over 800 units were produced, serving in the Atlantic, the Mediterranean, and the Pacific, and they provided valuable aerial reconnaissance during the Battle of the Falkland Islands and the Gallipoli Campaign. The Type 184’s versatility and combat achievements demonstrated the strategic value of carrier‑borne seaplanes, influencing post‑war naval aviation development worldwide. Its robust design also allowed adaptation to land‑plane configuration, and several were fitted with conventional wheeled undercarriages for training purposes.
Classification
Dimensions
- Length
- 487.5 inch
Performance
- Maximum Speed
- 88.5 mile per hour
- Service Ceiling
- 9000 foot
Production & History
- Units Produced
- 936
- First Flight
- 1915
Design & Classification
- Primary Use
- Manufacturer
- Short Brothers
- Engine
- Maori Mk.II
- Operator
-
Royal Naval Air Service
- Wikidata ID
- Q2279968