Sukhoi
Sukhoi UTB-2
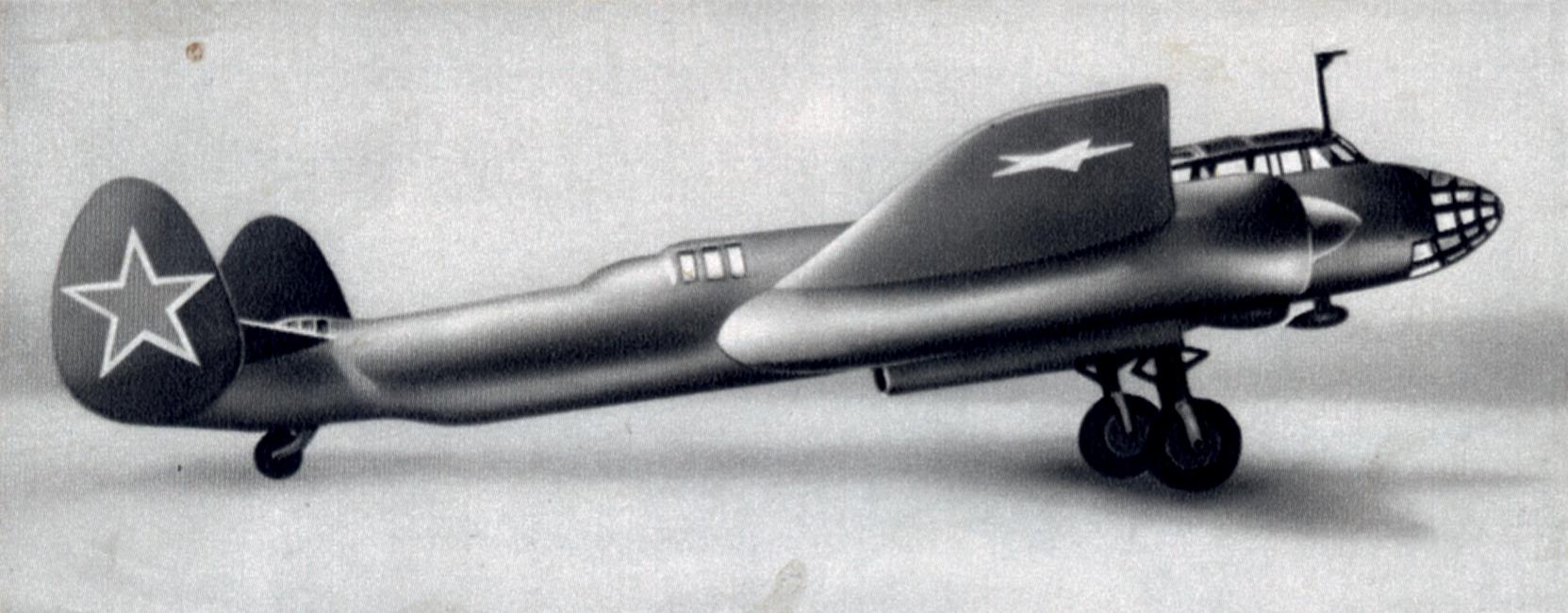
The Sukhoi UTB‑2 was an experimental twin‑engine bomber produced by the Sukhoi Design Bureau in the early 1940s. Conceived as a replacement for the aging DB‑3 series, the aircraft embodied a number of forward‑looking ideas that would later become hallmarks of Sukhoi’s design philosophy. Its airframe combined an all‑metal semi‑monocoque fuselage with a distinctive twin‑boom layout that housed the two Shvetsov M‑62 radial engines. Retractable main gear, a low‑set wing with a thin laminar‑flow profile, and flush‑mounted armament gave the UTB‑2 a clean aerodynamic shape and a top speed of about 620 km/h at 6 000 m. The prototype could carry a 500 kg bomb load and was defended by two 12.7 mm ShKAS machine guns in a dorsal turret and a ventral gondola. Only two airframes were completed; flight testing began in late 1942 but the program was cancelled in 1943 as Soviet industry shifted to mass‑producing proven types such as the Il‑2. Although it never entered service, the UTB‑2 supplied valuable data on high‑speed bomber aerodynamics and engine integration, feeding directly into later Sukhoi projects including the Su‑7 fighter‑bomber and the modern Su‑30 family. Its brief existence illustrates the experimental spirit that propelled Soviet aviation forward during World II.
Classification
Production & History
- Units Produced
- 176
- First Flight
- 1947
Design & Classification
- Country of Origin
- Manufacturer
- Sukhoi
- Engine
- Shvetsov ASh-21
- Operator
-
Polish Air Force Soviet Air Forces
- Wikidata ID
- Q2362737